Below is an analysis of their core components and the role of bus card readers within these systems.
Hardware Modules
Core Processor: Typically uses high-performance processors (e.g., ARM Cortex-M3 with a 120MHz clock speed) to ensure system stability and rapid response.
Display and Interaction Units: Include LCD screens (showing time, card number, balance, etc.), voice prompt modules (e.g., "Payment Successful" or "Insufficient Balance" alerts), and physical buttons (P+R design for enhanced usability).
Card Reader Module: Supports fast reading/writing of contactless IC cards (e.g., Mifare1, CPU cards, financial IC cards, NFC-enabled mobile cards), compliant with ISO 14443/7816 standards, with a reading distance of up to 50mm.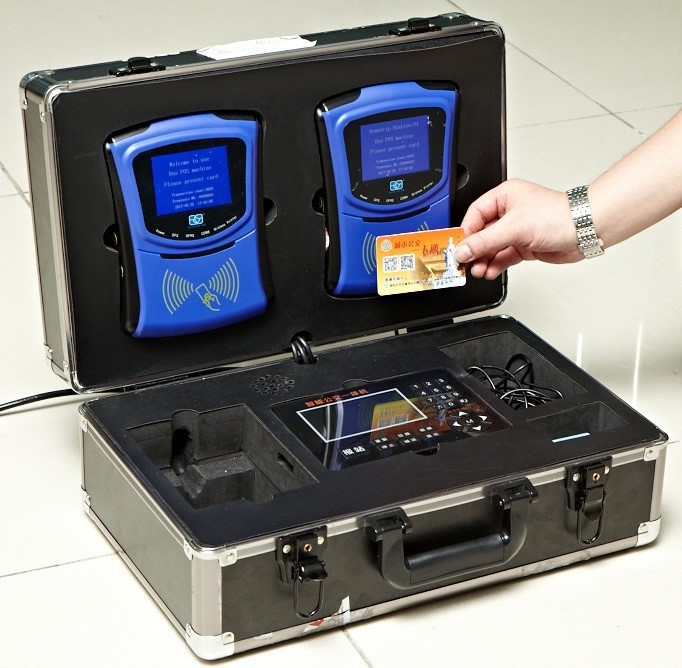
Communication Modules
Multi-mode Connectivity: Supports GPRS, CDMA, Zigbee, 4G, Wi-Fi, etc., for real-time data transmission, remote updates, and blacklist synchronization.
External Interfaces: Equipped with RS232 and USB ports for connecting GPS devices, dashcams, fare meters, and other peripherals.
Security and Authentication Modules
Dynamic Blacklist Management: Capable of storing up to 9.99 million blacklisted entries, automatically blocking unauthorized cards and triggering alarms.
PSAM Card Encryption: Features 4 PSAM card slots for secure transaction authentication via cryptographic keys.
Data Storage and Processing
Offline Storage: Stores up to 240,000 transaction records (older data is overwritten automatically); some models support SD card expansion up to 256MB.
Automated Statistics: Tracks driver attendance, operational revenue, and other metrics. Data can be extracted via USB or wireless channels.
Extended Functionality
Multi-scenario Adaptability: Supports operational strategies like segmented pricing, monthly passes, and transfer discounts.
Environmental Resilience: Designed for harsh vehicle conditions with a wide temperature range (-45℃ to 85℃), dustproof/waterproof housing, and shock resistance.
The bus card reader is a critical component of the in-vehicle terminal, serving the following functions:
Front-end Payment Interaction
Enables contactless fare deduction via cards or NFC devices, displaying real-time balances and supporting multiple payment modes (e.g., e-wallets, prepaid passes).
Provides multi-level voice prompts (e.g., "Invalid Card") and visual feedback via LED indicators (green/red lights).
Data Recording and Validation
Logs transaction details (card number, time, amount) for auditing and dispute resolution.
Verifies card legitimacy, blocks blacklisted/expired cards, and allows drivers to review transaction histories on-site.
Operational Management Support
Integrates with fleet management systems for driver sign-in/sign-out, shift scheduling, and attendance tracking.
Enables remote updates (e.g., fare adjustments, blacklist downloads) via wireless networks to streamline operations.
The in-vehicle intelligent fare collection terminal combines hardware, communication, and security modules to deliver efficient and secure public transport payment solutions. As its core interface, the bus card reader simplifies passenger transactions while fulfilling critical roles in data collection, security enforcement, and operational management. Together, they form an indispensable component in modern intelligent transportation systems.
More information, please check website: www.cardlangroup.com!
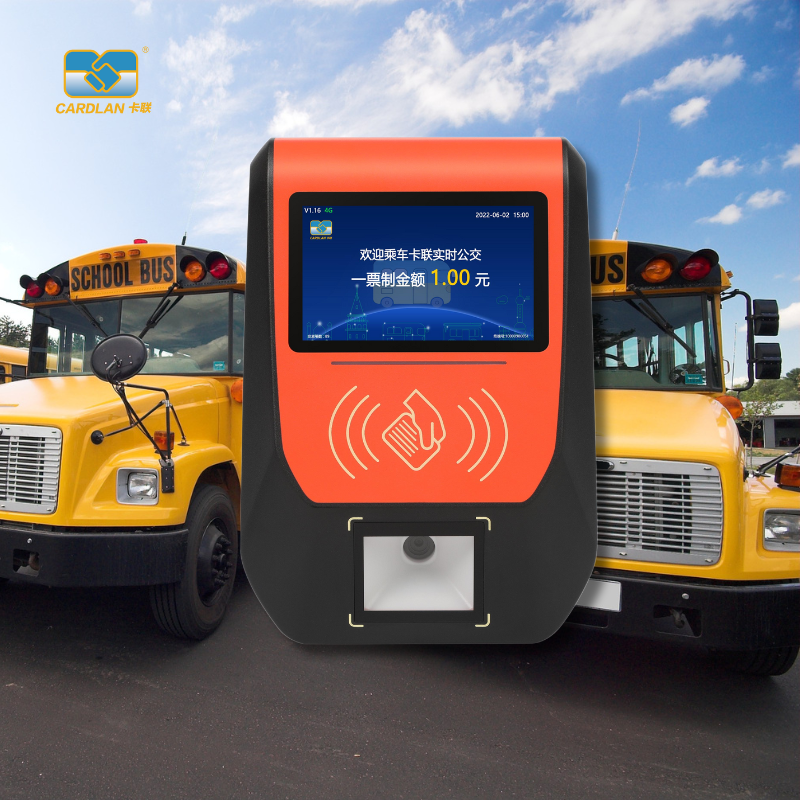 Cardlan Bus segment fare collection system
Cardlan Bus segment fare collection system
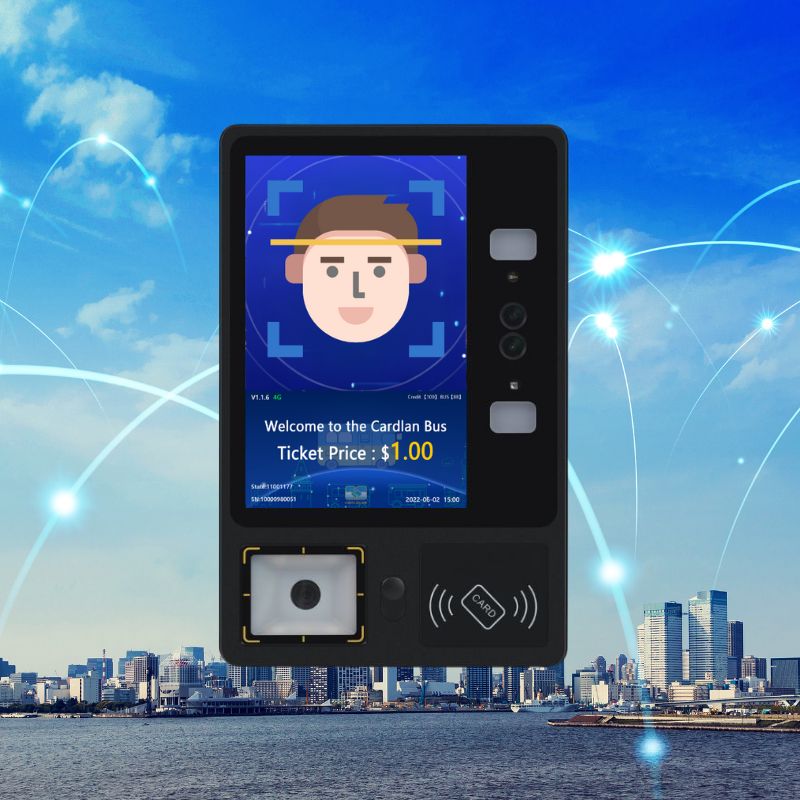 Cardlan bus card reader system
Cardlan bus card reader system
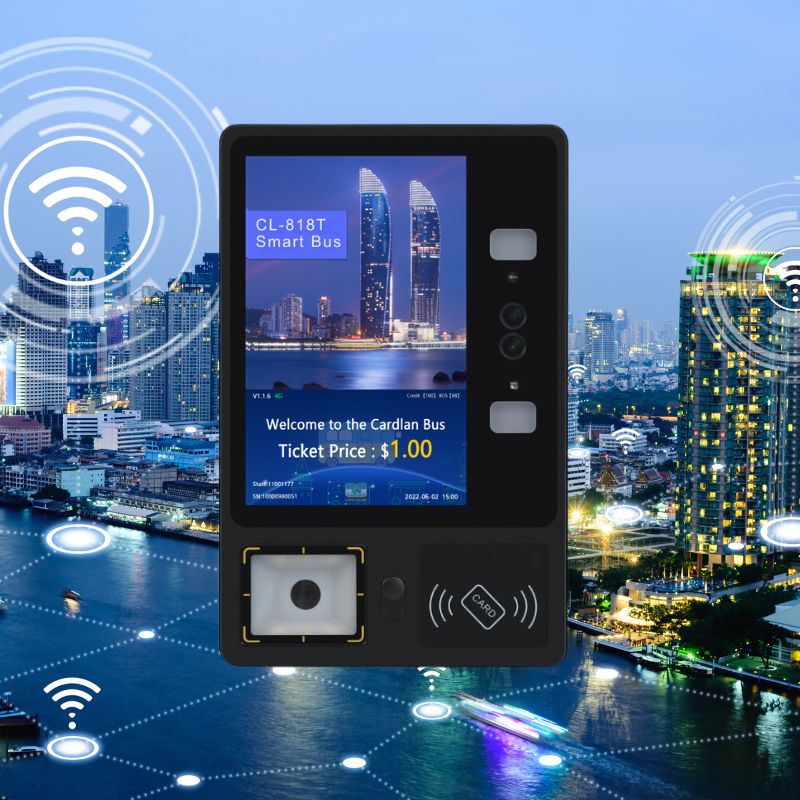 Cardlan Company: Strategic Deployment of Public Transportation Payment Products and Integrated Peripheral Devices (GPS Tracking, CCTV, Barriers)
Cardlan Company: Strategic Deployment of Public Transportation Payment Products and Integrated Peripheral Devices (GPS Tracking, CCTV, Barriers)
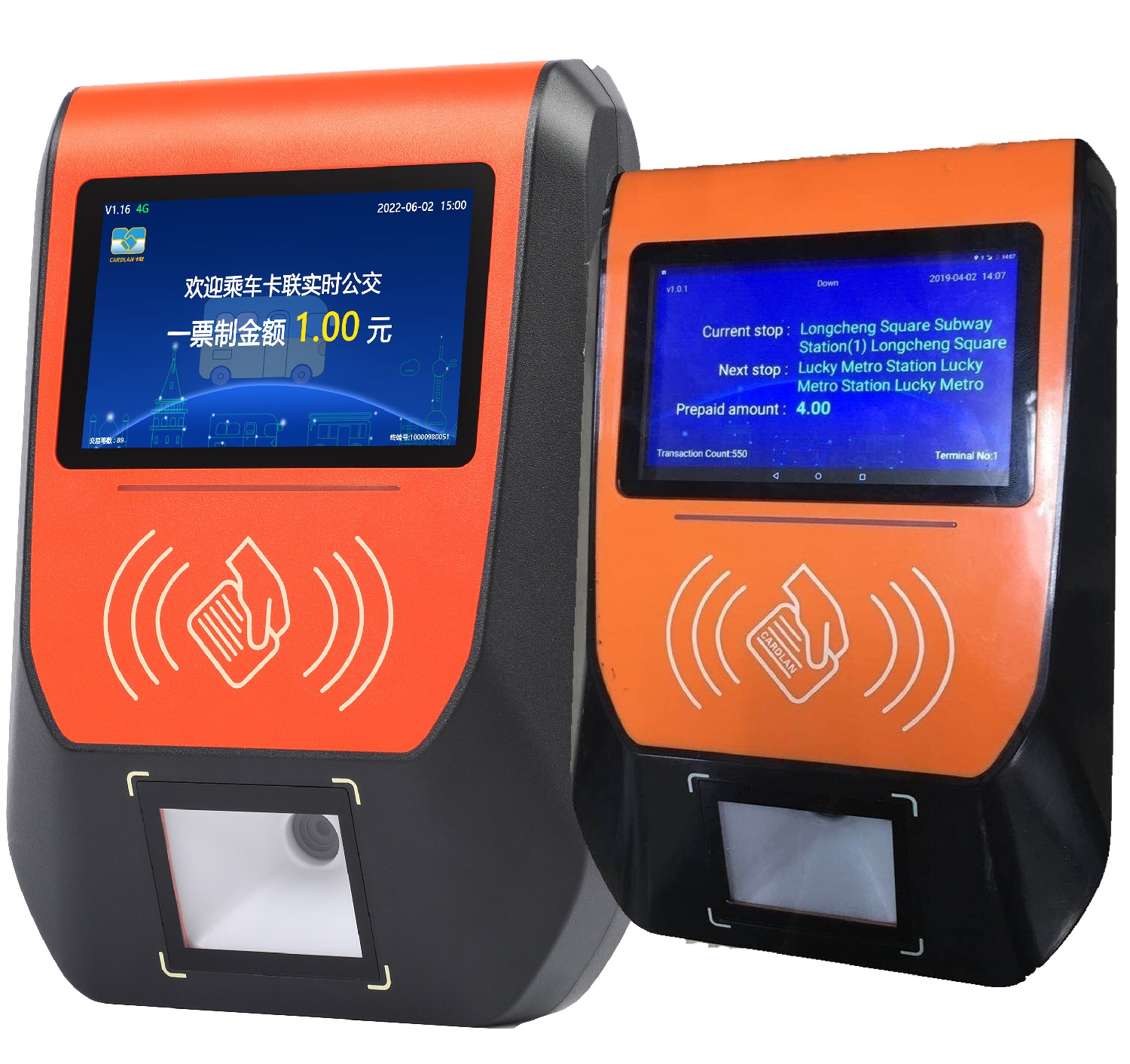 Cardlan 2026: Synergistic Innovation of Software Bus Fare System and Hardware OEM Production
Cardlan 2026: Synergistic Innovation of Software Bus Fare System and Hardware OEM Production